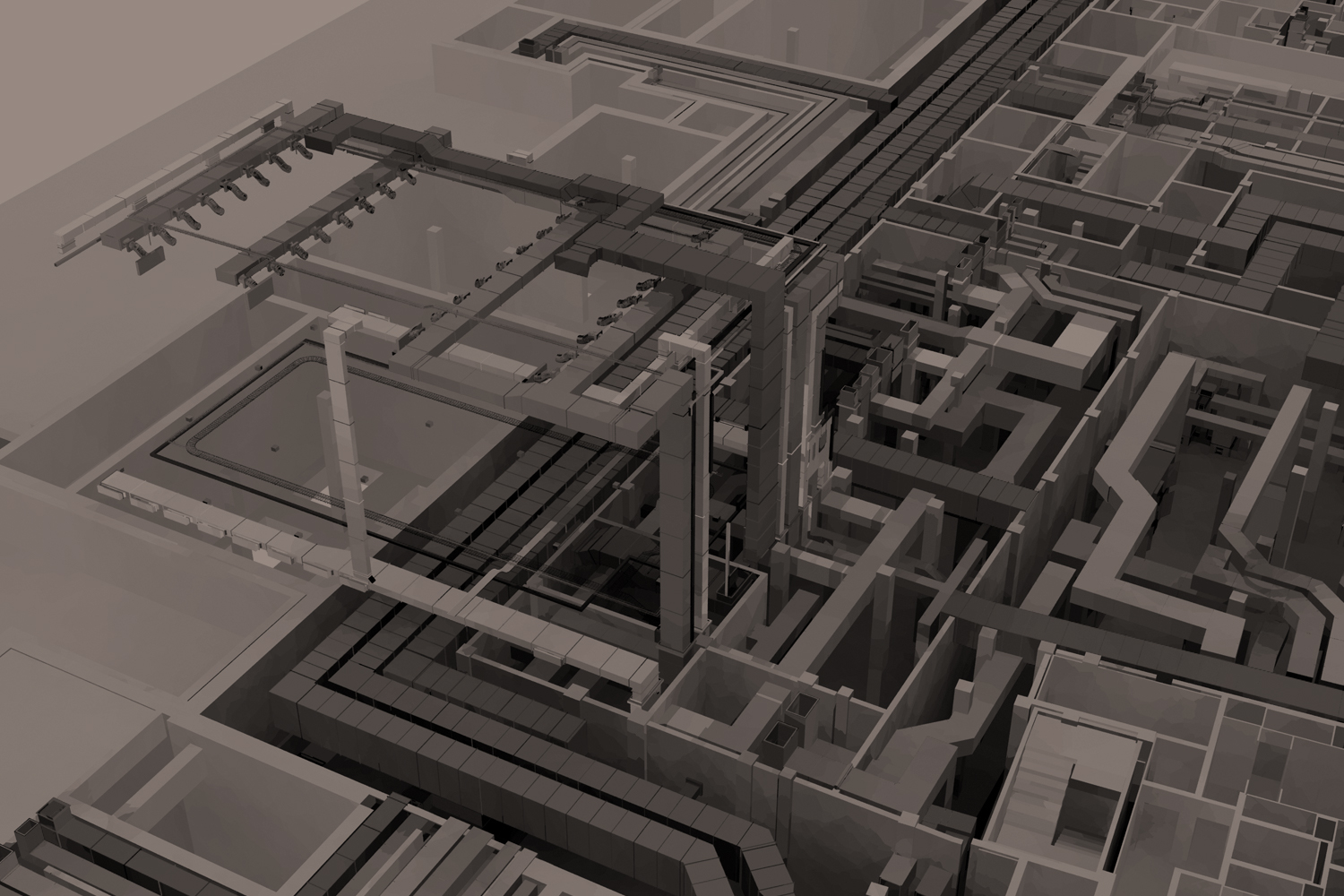
Building Information Modeling BIM has revolutionized the way architects, engineers, and construction professionals design, analyze, and construct buildings. In this article, we’ll delve into the key concepts and benefits of BIM specifically in the context of structural modeling.
Understanding BIM Structural Modeling
BIM is a digital representation of physical and functional characteristics of a building. When applied to structural engineering, BIM becomes a powerful tool for creating accurate 3D models of building structures. These models are intelligent, containing not just geometric information but also data about materials, quantities, performance specifications, and more.
Key components of BIM structural modeling include:
BIM structural modeling allows for parametric modeling, where elements in the model are defined by parameters such as size, shape, and relationship to other elements. Changes made to one part of the model automatically update related elements, ensuring consistency and accuracy throughout the design process.
Interoperability
BIM software facilitates collaboration and interoperability among different disciplines (architecture, structural engineering, MEP – mechanical, electrical, plumbing). Each discipline can work on their part of the model simultaneously, with changes reflected across the entire project in real-time.
Visualization and Simulation
BIM enables realistic visualization and simulation of structural behavior. Engineers can analyze how different loads, materials, or design changes affect the structure’s performance, leading to optimized designs and improved decision-making.
Data-Rich Models
BIM models contain a wealth of information beyond geometry. Structural elements are linked to databases with details like material properties, cost estimates, construction schedules, and maintenance requirements. This data can be leveraged throughout the building’s lifecycle.
Benefits of BIM Structural Modeling
The adoption of BIM in structural engineering brings numerous advantages:
Improved Collaboration
BIM fosters interdisciplinary collaboration, reducing conflicts and misunderstandings between architects, engineers, and contractors. By working on a shared platform, project stakeholders can coordinate more effectively, leading to smoother project delivery.
Enhanced Visualization
BIM’s 3D models enhance visualization and understanding of complex structural designs. Clients and project stakeholders can better comprehend the final product, reducing misinterpretations and change orders during construction.
Early Detection of Clashes
BIM software allows clash detection, where potential conflicts between structural, architectural, and MEP elements are identified before construction begins. This preemptive approach minimizes rework and ensures construction proceeds more efficiently.
Efficient Analysis and Optimization:
Structural analysis tools integrated into BIM software enable engineers to simulate various scenarios and optimize designs for performance, safety, and cost-efficiency. This iterative process results in more robust structures.
Cost and Time Savings
BIM facilitates accurate quantity take-offs, cost estimation, and construction scheduling. By identifying and resolving issues early in the design phase, costly delays and modifications during construction are minimized.
Lifecycle Management
BIM supports asset management throughout the building’s lifecycle. Maintenance schedules, renovation plans, and facility management tasks can be seamlessly integrated into the BIM model, ensuring the building remains efficient and well-maintained.
Real-World Applications
Large-Scale Infrastructure Projects
BIM is used in the design and construction of bridges, tunnels, and dams, enabling engineers to optimize complex structural systems and manage construction logistics.
High-Rise Buildings
BIM is invaluable for designing tall structures where structural integrity is critical. It allows for detailed analysis of wind and seismic loads, as well as efficient coordination of multiple building systems.
Renovation and Retrofitting
BIM facilitates renovation and retrofit projects by providing accurate as-built models, enabling designers to plan modifications with precision and minimizing disruption to ongoing operations.
Challenges and Future Trends
While BIM offers substantial benefits, its adoption also presents challenges:
Skill Requirements
BIM requires specialized skills and training. Professionals need to become proficient in BIM software and workflows to leverage its full potential. Integrating BIM across various platforms and software tools remains a challenge. Standardization efforts are ongoing to improve interoperability.
Looking ahead, the future of BIM in structural modeling is promising. Emerging technologies like generative design, artificial intelligence, and cloud-based collaboration will further enhance BIM’s capabilities, enabling more efficient and sustainable construction practices.
Conclusion
BIM structural modeling is transforming the way structural engineers design, analyze, and manage buildings. By leveraging parametric modeling, interdisciplinary collaboration, and data-rich models, BIM optimizes project delivery, enhances structural performance, and supports sustainable building practices. As the construction industry embraces digital transformation, BIM will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping the built environment of tomorrow.