In today’s fast-paced construction industry, collaboration is key to success. With the advent of Building Information Modeling (BIM), collaboration has been taken to new heights, particularly in the realm of structural engineering. Structural BIM services offer a multitude of benefits, from enhanced coordination and communication to improved efficiency and cost savings. In this blog post, we’ll delve into how leveraging structural BIM services can transform collaboration in construction projects.
What is BIM?
Before diving into the specifics of structural BIM services, let’s briefly define what BIM is. Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a building. It’s a collaborative process that allows multiple stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and owners, to work together on a construction project.
The Role of BIM in Structural Engineering
In structural engineering, BIM serves as a powerful tool for streamlining the design, analysis, and documentation processes. Structural BIM models contain detailed information about the building’s structural components, including beams, columns, slabs, and connections. This rich data facilitates better decision-making and enables engineers to identify and resolve conflicts early in the design phase.
Enhanced Collaboration through Structural BIM Services
Improved Communication: Structural BIM models serve as a centralized repository of information that can be accessed and updated by all project stakeholders in real-time. This eliminates the need for cumbersome email chains and allows team members to communicate more effectively. Whether it’s discussing design changes, resolving clashes, or sharing updates, structural BIM fosters seamless communication among architects, engineers, and contractors.
Coordination Across Disciplines
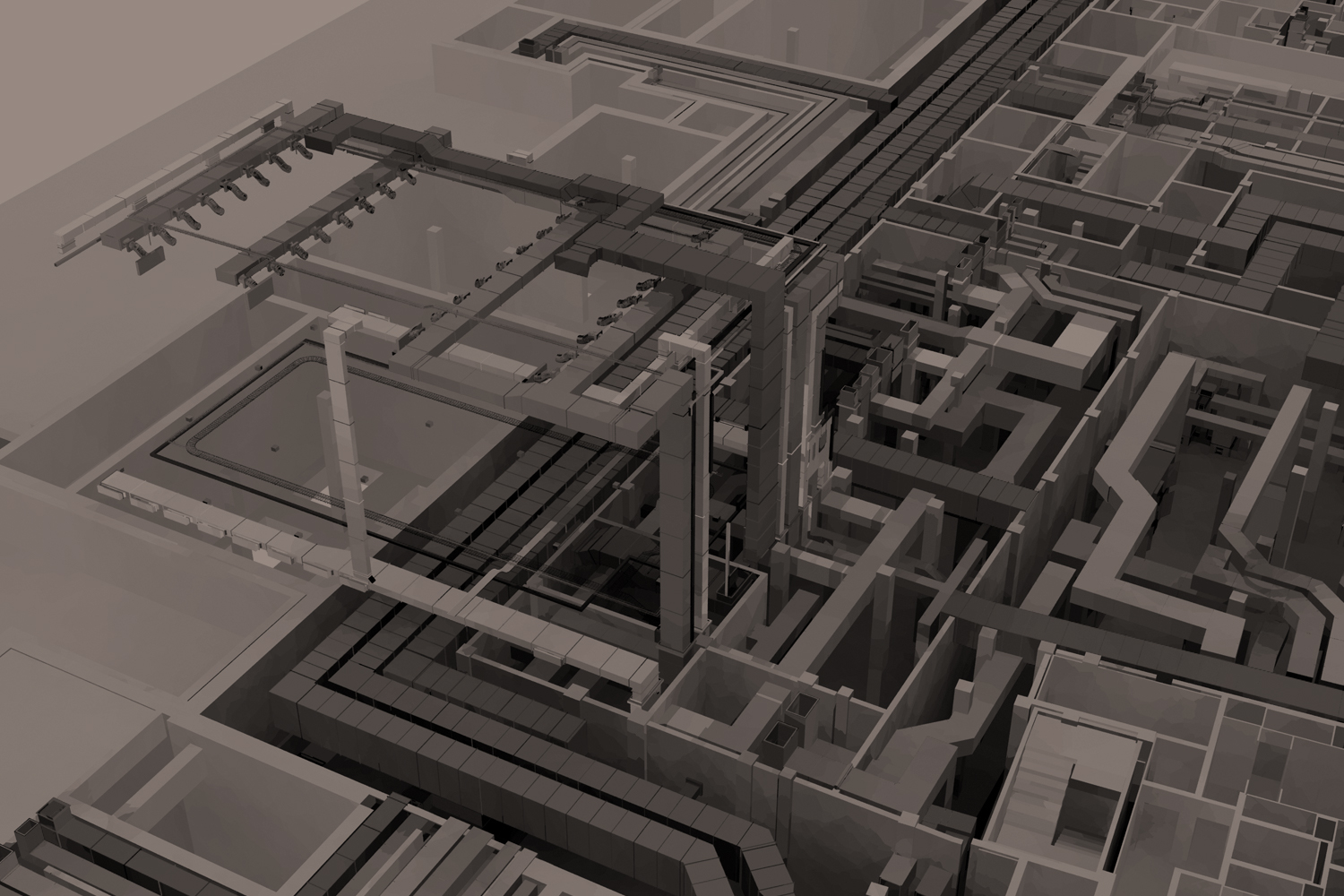
In a construction project, various disciplines, such as architecture, structural engineering, and MEP (mechanical, electrical, plumbing) systems, need to work together harmoniously. Structural BIM facilitates interdisciplinary coordination by integrating models from different disciplines into a single, federated model. This ensures that all components of the building are properly coordinated, minimizing clashes and reducing rework during construction.
Clash Detection and Resolution
One of the most significant benefits of Structural BIM services is the ability to detect and resolve clashes between different building systems before construction begins. Clash detection tools analyze the BIM model to identify conflicts such as interference between structural elements, clash with MEP systems, or spatial conflicts between architectural features. By addressing these clashes early in the design phase, costly errors and delays during construction can be avoided.
Visualizing Complex Structures
Structural BIM models provide a 3D visualization of the building’s structure, allowing stakeholders to better understand complex geometries and structural systems. This visual representation enhances communication and enables stakeholders to make informed decisions about the design and construction process. Whether it’s evaluating alternative structural systems or simulating construction sequences, 3D visualization helps teams visualize the project’s intricacies and identify potential challenges.
Quantification and Cost Estimation
Beyond design and coordination, structural BIM models can also be leveraged for quantity takeoffs and cost estimation. By associating material quantities with elements in the BIM model, engineers can generate accurate bill of quantities (BOQ) and cost estimates for the project. This enables owners and contractors to better understand project costs and make informed decisions about budgeting and procurement. By utilizing structural BIM services, the engineering team collaborates closely with architects and MEP engineers to develop a coordinated BIM model. Clash detection tools identify clashes between structural elements and MEP systems, which are promptly resolved through collaboration among the project team. This early clash detection prevents costly rework during construction and ensures that the building systems fit seamlessly within the structural framework.
Furthermore the 3D visualization capabilities of structural BIM enable stakeholders to visualize the building’s complex structural geometry and make informed decisions about design modifications. Quantification tools integrated into the BIM model allow the engineering team to generate accurate material takeoffs and cost estimates, providing the owner with greater visibility into project costs.
Conclusion
Structural BIM services play a crucial role in enhancing collaboration in construction projects. By improving communication, facilitating interdisciplinary coordination, enabling clash detection and resolution, visualizing complex structures, and supporting quantity takeoffs and cost estimation, BIM technology transforms the way structural engineers work. As the construction industry continues to embrace digitalization, the adoption of structural BIM services will become increasingly essential for delivering successful projects on time and within budget.