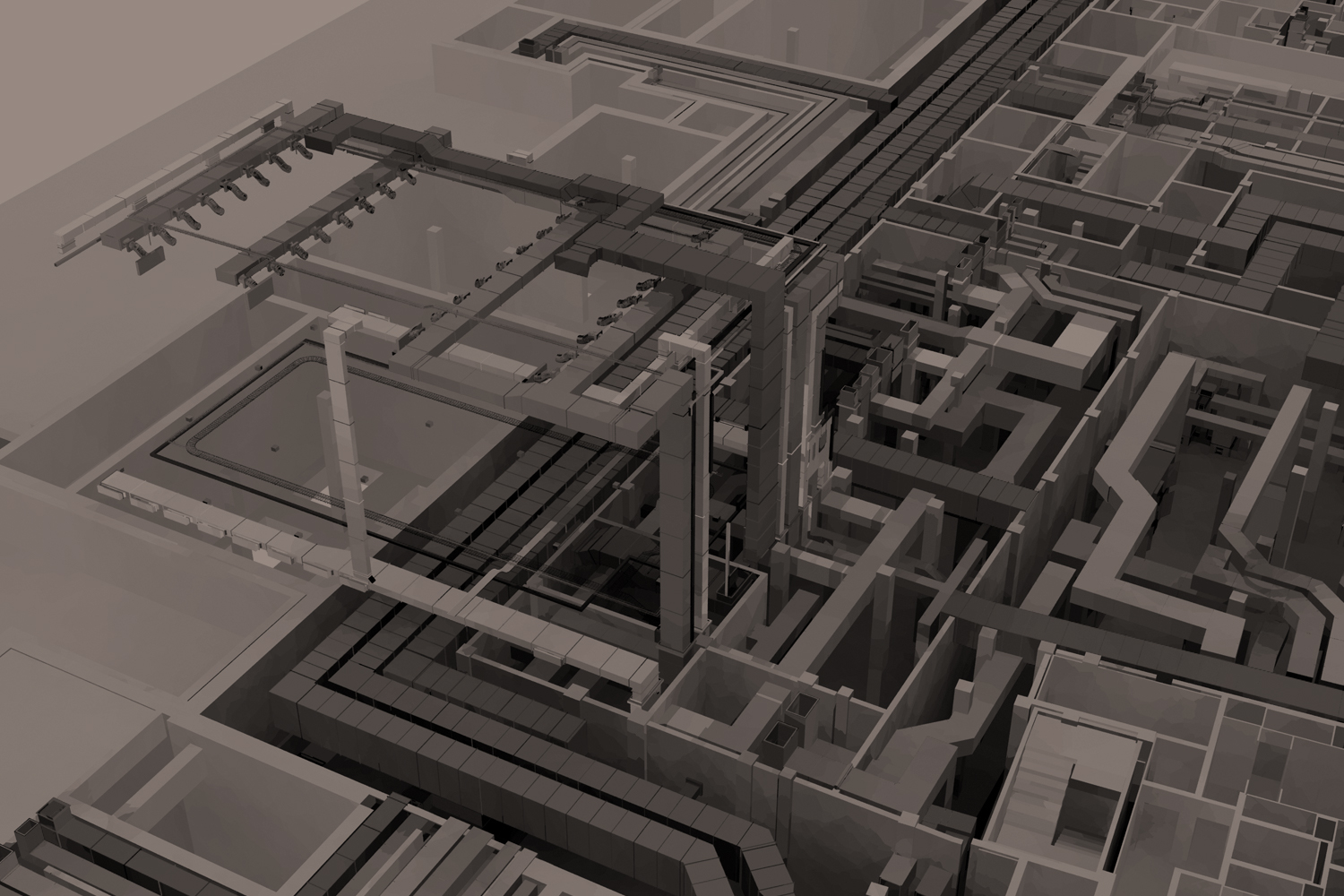
In the realm of construction, embracing technological advancements is pivotal for progress. Among these advancements, Building Information Modeling (BIM) stands out as a transformative force, revolutionizing how construction projects are conceptualized, planned, and executed. Let’s delve into the latest innovations within the realm of BIM and their profound impact on the construction landscape.
Understanding BIM A Paradigm Shift in Construction
At its core, BIM is not merely a tool but a methodology—a collaborative approach that enables stakeholders to create and manage digital representations of physical and functional characteristics of a project. Unlike traditional 2D blueprints, BIM creates a digital twin of a structure, integrating geometric and non-geometric data to offer a comprehensive view of the entire project lifecycle.
Parametric Design and Generative Modeling
Recent BIM innovations have focused on enhancing design capabilities. Parametric design within BIM enables architects and engineers to create intelligent, algorithm-driven designs that adjust and adapt based on specified parameters. Generative modeling takes this a step further, exploring countless design iterations to optimize outcomes based on performance and efficiency metrics.
Cloud-Based Collaboration and Integration
The migration of BIM processes to cloud-based platforms has been a game-changer. Cloud-enabled BIM facilitates seamless collaboration among project stakeholders, regardless of geographical location. This integration ensures real-time access to project data, fostering enhanced communication, and eliminating the silos that often impede traditional project management.
Advancements in Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
BIM innovations have intersected with VR and AR technologies, offering immersive experiences that transform project visualization. VR allows stakeholders to virtually immerse themselves in designs, facilitating better understanding and decision-making. AR overlays digital data onto physical spaces, enabling stakeholders to view proposed designs within existing environments, aiding in better contextualization and comprehension.
Data Analytics and Predictive Modeling
BIM’s integration with data analytics has unlocked a treasure trove of insights. Predictive modeling harnesses vast amounts of project data to foresee potential issues, optimize schedules, mitigate risks, and enhance project performance. By leveraging historical project data, BIM-driven predictive analytics enable informed decision-making throughout the project lifecycle.
Sustainability and Performance Optimization
Innovations in BIM have been pivotal in driving sustainability initiatives within construction. BIM’s ability to simulate energy consumption, daylighting, and material efficiency facilitates the creation of environmentally conscious designs. By analyzing various design iterations, BIM aids in optimizing building performance to meet stringent sustainability standards.
Automation and Robotics in Construction
The incorporation of automation and robotics into BIM processes streamlines construction operations. From robotic construction crews capable of executing repetitive tasks with precision to automated material handling within BIM frameworks, these innovations minimize errors, reduce labor costs, and expedite project timelines.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While BIM innovations have revolutionized the construction industry, challenges persist. These include interoperability issues between various BIM software platforms, the need for standardized data formats, cybersecurity concerns, and the learning curve associated with adopting advanced technologies. Looking ahead, the future of BIM lies in further integration with emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT). The convergence of these technologies is poised to push the boundaries of what’s achievable within the realm of construction.
Interoperability and Standardization
One of the key challenges faced in BIM innovation is the need for greater interoperability and standardization among various software platforms. Different stakeholders often use disparate BIM tools, leading to compatibility issues and hindering seamless data exchange. Efforts to establish standardized data formats and protocols are crucial to overcome these challenges, enabling smoother collaboration and data sharing across the construction ecosystem.
Cybersecurity Concerns
As BIM processes increasingly rely on cloud-based platforms and interconnected systems, cybersecurity becomes a significant concern. Safeguarding sensitive project data from potential cyber threats and ensuring the integrity of BIM models demand robust security measures. Industry-wide standards and protocols for data encryption, access control, and secure data sharing are vital to mitigate these risks.
Skill Development and Adoption
The widespread adoption of BIM innovations necessitates a skilled workforce capable of leveraging these technologies effectively. Training programs, certifications, and continuous education initiatives are essential to equip professionals with the necessary expertise in using advanced BIM tools. Bridging the gap between traditional construction practices and cutting-edge technologies remains a challenge, emphasizing the need for ongoing skill development efforts.
Enhanced Predictive Analytics
The integration of machine learning and AI into BIM processes holds immense promise. Predictive analytics, powered by AI algorithms, can analyze vast datasets from previous projects to anticipate potential issues, optimize project schedules, and offer predictive maintenance insights. These advancements in data-driven decision-making have the potential to revolutionize project planning and execution.
Regulatory and Cultural Shifts
Adopting BIM innovations often requires regulatory adaptations and cultural shifts within the construction industry. Encouraging regulatory bodies to standardize requirements and incentivize BIM adoption, while simultaneously fostering a culture of innovation and openness to new technologies among industry professionals, remains crucial for widespread implementation.
The Future Trajectory
Looking ahead, BIM’s evolution seems inexorably linked to technological convergence. Integrating BIM with IoT sensors for real-time data collection, AI-driven predictive analytics, and robotics for on-site construction tasks heralds a future where construction processes are more automated, data-driven, and efficient.
Conclusion
The ongoing innovations within BIM underscore its indispensable role in the construction sector’s evolution. ENGISOFT ENGINEERING – BIM Staffing & BIM Services by continually pushing the envelope in design capabilities, collaboration, data utilization, sustainability, and automation, BIM remains at the forefront of transforming construction practices. As the construction industry embraces these BIM innovations, stakeholders can anticipate streamlined processes, reduced costs, improved project outcomes, and a more sustainable approach to building the structures of tomorrow.